
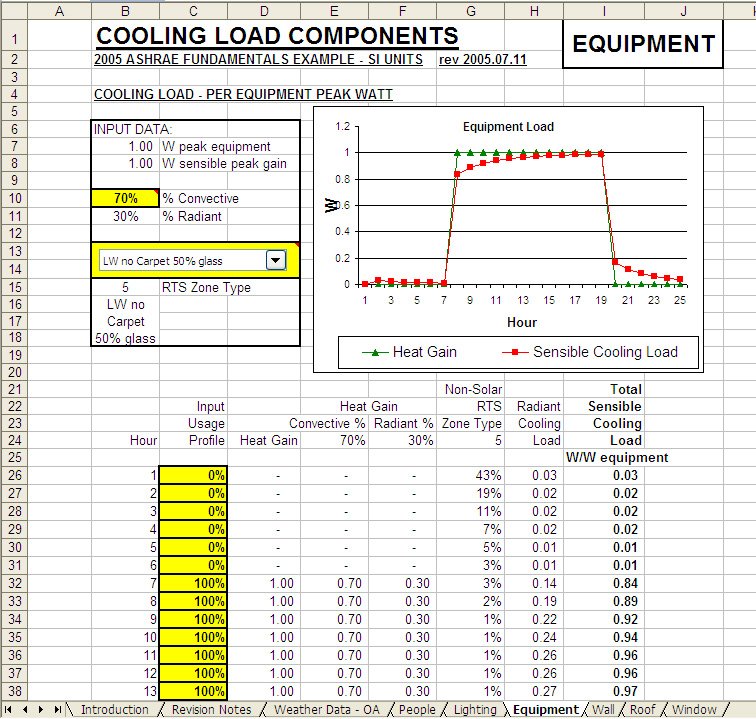
The radiant time series (RTS) method is a simplified method for performing design cooling load calculations that are derived from the heat balance (HB) method. These heat sources may be radiant and convective loads from lighting and transformers conduction loads from adjacent walls, roofs, or glazing or duct and piping systems within the plenum.Radiant time series method for Indian condition Unlike a traditional ducted return, the plenum may have multiple heat sources in the path. The space above a ceiling, when used as a return air path, is a ceiling return air plenum. in a different zone), heat transfer through the separating physical section must be considered. Whenever a conditioned space is adjacent to a space with a different temperature (i.e. Sol-air temperature is the outdoor air temperature that, in the absence of all radiation changes, gives the same rate of heat entry into the surface as would the combination of incident solar radiation, radiant energy exchange with the sky and other outdoor surroundings, and convective heat exchange with outdoor air.Ĭonduction through exterior walls and roofs is calculated using conduction time series (CTS). It differs primarily as a function of the mass and nature of the wall or roof construction, because those elements affect the rate of conductive heat. Heat gain through exterior opaque surfaces is derived from the same elements of solar radiation and thermal gradient as that for fenestration areas.


The engine repeats this process for multiple design months to determine the month when the peak load occurs.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
